Tim akuisisi bakat terjebak dalam siklus tekanan yang meningkat. Menurut SHRM, kandidat yang paling memenuhi syarat seringkali keluar dari pasar dalam waktu 10 hari, namun proses perekrutan rata-rata bisa berlarut-larut hingga lebih dari 40 hari. Kesenjangan ini menciptakan serangkaian biaya yang mahal. tantangan rekrutmen. Proses perekrutan yang panjang berarti talenta terbaik menerima tawaran dari pesaing yang lebih gesit. Kerugian ini, ditambah dengan kurangnya pelamar yang memenuhi syarat, menciptakan tekanan besar untuk “sewa cepat“, seringkali tanpa tujuan perekrutan yang jelas untuk memandu pengambilan keputusan.

This reactive, “fire-fighting” approach is the primary cause of poor hiring outcomes. It leads to “skill mismatches,” poor cultural fits and, ultimately, “high turnover and low retention”. This revolving door of talent restarts the entire, costly process. The problem is not just that hiring is difficult. It is that a reactive, goalless hiring process is fundamentally designed to fail.
Penangkal strategis untuk lingkaran setan ini adalah penerapan tujuan rekrutmen yang jelas dan berbasis data. Dengan beralih dari ambisi yang samar ke strategi proaktif yang dibangun di atas kerangka kerja SMART, tim dapat memutus siklus tersebut.
TL;DR – SMART Recruitment Goals for 2026
Recruitment in 2026 demands precision, speed and measurable impact. SMART recruitment goals transform hiring from reactive decision-making into a structured, data-driven strategy aligned with business growth.
- Tujuan SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) turn vague hiring intentions into actionable, trackable business objectives.
- The 5 core recruitment focus areas for 2026: Time-to-Fill, Quality of Hire, Cost-per-Hire, Candidate Experience and Diversity & Inclusion.
- Start with a baseline audit of your current hiring metrics before setting new targets.
- Align every recruitment goal with broader organizational objectives and OKRs.
- Track progress using data from your Sistem Pelacakan Pelamar (ATS) and HR analytics dashboard.
- Use a balanced scorecard approach to avoid optimizing one metric (e.g., speed) at the expense of another (e.g., quality).
- AI-powered sourcing, structured interviews and automated reporting will be key competitive advantages in 2026.
👉 In short: Shift from reactive hiring to a structured SMART framework that improves efficiency, quality and long-term workforce performance.
Apa Sasaran Rekrutmen (Dan Mengapa Membuatnya “SMART”)?
Recruitment goals are measurable hiring objectives set by HR teams to improve hiring speed, quality, cost efficiency, diversity and candidate experience, aligned with overall business strategy using the SMART framework.
Sasaran rekrutmen adalah tujuan spesifik yang ditetapkan oleh tim sumber daya manusia atau akuisisi bakat untuk memandu dan meningkatkan keseluruhan proses perekrutan. Tujuan dari sasaran ini adalah untuk meningkatkan kinerja tim, menyederhanakan proses, dan yang terpenting, memastikan bahwa semua upaya perekrutan selaras langsung dengan kebutuhan strategis organisasi yang lebih luas.
Why Use the SMART Framework?
Yang utama masalah yang dihadapi banyak tim SDM Tujuan mereka sebenarnya hanyalah angan-angan. Tujuan seperti "mempekerjakan orang yang lebih baik" atau "mempercepat perekrutan" hanyalah ambisi yang samar, bukan tujuan bisnis yang dapat ditindaklanjuti. Ketidakjelasan ini secara langsung menyebabkan kesenjangan komunikasi dan hambatan pengambilan keputusan yang mengganggu tim SDM.
Inilah sebabnya mengapa CERDAS kerangka: Spesifik, Terukur, Dapat Dicapai, Relevan dan Terikat Waktu adalah mekanisme penting untuk mengubah keinginan tersebut menjadi tujuan fungsional.
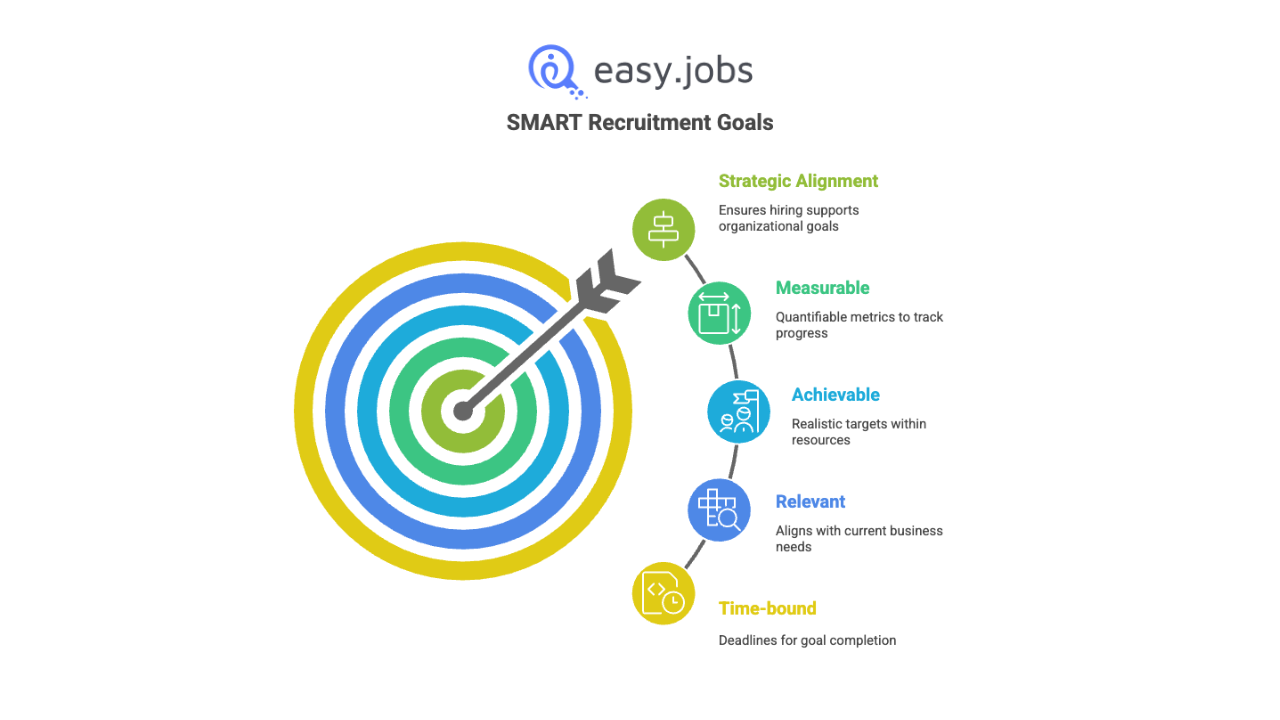
Recruitment Goals vs Recruitment KPIs
| Recruitment Goals | Recruitment KPIs |
|---|---|
| Strategic objectives | Performance metrics |
| Long-term direction | Quantitative measurement |
| Example: Reduce time-to-fill | Example: Average days to hire |
Sasaran SMART tidak berdiri sendiri. Sasaran ini berfungsi dalam hierarki strategis yang jelas, mengalir dari tingkat tertinggi organisasi. Memahami hierarki ini memberikan konteks penting:
- Tujuan Organisasi: Misi strategis tingkat tinggi perusahaan (misalnya, “Meningkatkan efisiensi operasional”).
- OKR Departemen (Tujuan dan Hasil Utama): Bagaimana departemen SDM akan berkontribusi pada misi tersebut (misalnya, “Meningkatkan perolehan bakat”).
- Tujuan Rekrutmen SMART: Inisiatif spesifik dan dapat ditindaklanjuti untuk mencapai OKR tersebut (misalnya, “Kurangi waktu pengisian untuk semua posisi yang terbuka sebesar 25% pada akhir tahun”).
- KPI (Indikator Kinerja Utama) Perekrutan: Metrik spesifik yang digunakan untuk melacak kemajuan terhadap sasaran SMART (misalnya, “Waktu Pengisian dalam hari”).
Cara Menetapkan Sasaran Rekrutmen SMART: Panduan 5 Langkah

Menetapkan tujuan yang efektif adalah proses analisis, penyelarasan, dan komunikasi yang terstruktur. Panduan langkah demi langkah ini menyediakan kerangka kerja untuk menciptakan tujuan yang ambisius sekaligus dapat ditindaklanjuti.
Langkah 1: Analisis Kinerja Anda Saat Ini (Tetapkan Dasar Anda)
It is impossible to set a measurable goal without first knowing the starting point. An objective to “reduce” time-to-fill from 45 days is meaningless if the current baseline is not known. This first step involves conducting a baseline audit of key recruitment metrics. Before setting new goals, the team must answer:
- Berapa rata-rata Waktu Pengisian dan Waktu Perekrutan saat ini?
- Apa arus saat ini? Biaya per Sewa?
- Bagaimana Kualitas Perekrutan saat ini, yang diukur dari tingkat pergantian karyawan di tahun pertama dan kepuasan manajer perekrutan?
Langkah 2: Menyelaraskan Tujuan dengan Tujuan Bisnis
Langkah ini mewakili "R" (Relevan) dalam SMART pada tingkat makro. Untuk mengamankan penerimaan dan menunjukkan ROI, tujuan rekrutmen harus bermuara langsung dari strategi menyeluruh perusahaan.
Penyelarasan ini memerlukan pertanyaan: “Apa yang ingin dicapai oleh bisnis, dan bagaimana akuisisi bakat dapat membantu kita mencapainya?”
- Jika tujuan bisnisnya adalah: “Ekspansi ke pasar baru,”
- Tujuan perekrutan haruslah: “Membangun jalur bakat pasif yang berkualitas di wilayah target tersebut”.
- Jika tujuan bisnisnya adalah: “Meningkatkan profitabilitas perusahaan,”
- Tujuan perekrutan haruslah: “Kurangi Biaya per Perekrutan rata-rata sebesar 15% dengan meningkatkan saluran sumber daya berbiaya rendah”.
Langkah 3: Dekonstruksi Tujuan Anda dengan Kerangka Kerja SMART
This is the core collaborative exercise. One of the most significant pain points in recruiting is the “communication gap” between recruiters and hiring managers, which often manifests as “unrealistic expectations“.
The solution is co-writing the SMART goal with these stakeholders. It forces alignment before the search begins. By agreeing on what is “Dapat dicapai" Dan "Relevant,” all parties are held accountable to a shared, clearly defined objective. Use these guiding questions for each component:
- Spesifik (S): Apa sebenarnya yang perlu dicapai? Siapa yang bertanggung jawab? Peran, departemen, atau proses mana yang terpengaruh?
- Terukur (M): Bagaimana kesuksesan akan diukur? Apa metriknya (KPI) dan targetnya (angka, persentase, atau jumlah dolar)?
- Dapat dicapai (A): Apakah tujuan ini realistis mengingat sumber daya yang tersedia (tim, anggaran, alat perekrutan)? Tindakan, strategi, atau sumber daya baru apa yang diperlukan untuk mewujudkannya?
- Relevan (R): Mengapa tujuan ini penting? Apakah tujuan ini secara langsung mendukung tujuan bisnis yang lebih luas yang diidentifikasi pada Langkah 2?
- Terikat waktu (T): Kapan batas waktunya? Apa saja tonggak penting atau tanggal check-in?
Langkah 4: Tulis Pernyataan Tujuan SMART Akhir Anda
Setelah menguraikan tujuan, gabungkan jawaban dari Langkah 3 menjadi satu pernyataan tunggal yang jelas dan tidak ambigu. Pernyataan ini menjadi arahan tim.
Misalnya, tujuan yang samar seperti “mempekerjakan peran teknis lebih cepat” menjadi tujuan SMART: “Mengurangi waktu pengisian rata-rata untuk semua posisi teknis (S) dari 45 hari menjadi 30 hari (M) dengan menerapkan alat sumber AI baru (A) untuk mencegah kehilangan kandidat terbaik (R) pada akhir Q3 (T)”.
Step 5: Allocate Resources, Communicate the Goal And Track Progress
Suatu tujuan tidak akan berguna jika tidak diimplementasikan. Langkah terakhir ini melibatkan tindakan:
- Alokasikan Sumber Daya: Dedikasikan sumber daya yang diidentifikasi pada langkah “Dapat Dicapai”, seperti membeli sistem pelacakan pelamar (ATS) baru atau berinvestasi dalam pelatihan.
- Menyampaikan: Bagikan tujuan akhir tertulis dengan semua pemangku kepentingan, termasuk tim TA, manajer perekrutan, dan pimpinan eksekutif, untuk memastikan keselarasan.
- Melacak: Tetapkan irama teratur (misalnya, mingguan atau bulanan) untuk meninjau KPI yang terkait dengan tujuan dan menyesuaikan strategi seperlunya.
5 Tujuan Umum Rekrutmen SMART (Pendekatan Balanced Scorecard)
Lima tujuan rekrutmen yang paling umum: Waktu, Kualitas, Biaya, Pengalaman, dan Keberagaman. Ini bukan sekadar contoh yang terisolasi. Kelima tujuan ini mewakili ketegangan inti dalam akuisisi bakat. Strategi rekrutmen yang matang menggunakan pendekatan "balanced scorecard" untuk mengelolanya.
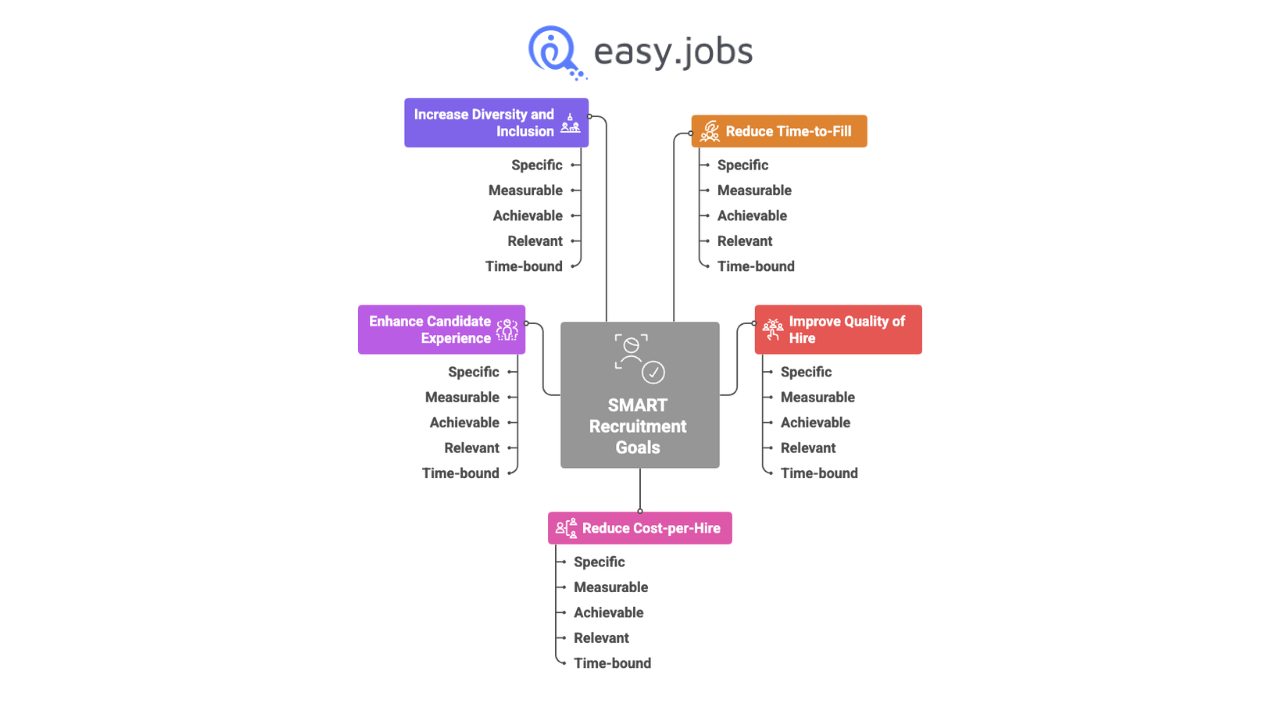
Focusing exclusively on one goal will inevitably damage another. For instance, a myopic focus on “Reduce Time-to-Fill” can lead to rushed hires and damage “Kualitas Sewa“. Conversely, a search for the “perfect candidate” can extend Time-to-Fill indefinitely. The following examples demonstrate how to set goals for each of these areas as part of a balanced portfolio.
1. Reduce Time-to-Fill
- Tujuan Umum: Percepat proses perekrutan untuk mengamankan bakat terbaik sebelum pesaing.
- S (Spesifik): Mengurangi waktu rata-rata untuk mengisi semua posisi penjualan yang terbuka.
- M (Terukur): Dari dasar saat ini 50 hari menjadi 35 hari, diukur dengan analisis ATS.
- A (Dapat dicapai): Hal ini dapat dicapai melalui penerapan program rujukan karyawan baru yang diberi insentif, dan mengotomatisasi penyaringan awal menggunakan alat yang digerakkan oleh AI.
- R (Relevan): Hal ini relevan untuk mencegah hilangnya kandidat terbaik di pasar yang kompetitif dan untuk mengisi peran yang menghasilkan pendapatan dengan lebih cepat, yang secara langsung berdampak pada laba perusahaan.
- T (Terikat waktu): Dalam 6 bulan ke depan (akhir Q4).
- Sasaran SMART Akhir: “Kurangi waktu rata-rata pengisian posisi penjualan dari 50 menjadi 35 hari pada akhir Q4, dengan meluncurkan program rujukan karyawan baru dan menerapkan alat pencarian yang didukung AI.”
2. Improve Quality of Hire (QoH)
- Tujuan Umum: Rekrut kandidat yang lebih baik yang berkinerja baik dan bertahan lebih lama di perusahaan.
- S (Spesifik): Tingkatkan tingkat retensi 1 tahun untuk karyawan baru di departemen teknik.
- M (Terukur): Dari dasar saat ini 75% menjadi 90%, diukur berdasarkan data retensi HRIS dan survei kepuasan manajer perekrutan selama 6 bulan.
- A (Dapat dicapai): Hal ini dapat dicapai dengan mengganti wawancara tidak terstruktur dengan wawancara terstruktur berbasis keterampilan yang terstandarisasi, dan mengadopsi filosofi “prinsip pertumbuhan” yang merekrut orang-orang dengan potensi tinggi, bukan hanya mereka yang memiliki kecocokan sempurna dengan resume mereka.
- R (Relevan): Hal ini relevan untuk mengurangi tingginya biaya finansial dan budaya akibat pergantian karyawan dan meningkatkan produktivitas tim jangka panjang.
- T (Terikat waktu): Untuk semua perekrutan yang dilakukan pada tahun fiskal ini, dengan keberhasilan diukur pada ulang tahun pertama.
- Sasaran SMART Akhir: “Tingkatkan tingkat retensi 1 tahun untuk perekrutan teknisi baru dari 75% menjadi 90% untuk semua perekrutan yang dilakukan pada tahun fiskal ini, dengan menerapkan wawancara terstruktur berbasis keterampilan yang wajib dan memantau kepuasan manajer selama 6 bulan.”
3. Reduce Cost-per-Hire (CPH)
- Tujuan Umum: Optimalkan pengeluaran perekrutan dan buat proses perekrutan lebih efisien secara finansial.
- S (Spesifik): Turunkan biaya rata-rata per perekrutan untuk semua peran non-eksekutif.
- M (Terukur): Oleh 15%, dari rata-rata $4.000 menjadi $3.400, dihitung menggunakan rumus CPH standar: (Biaya Internal + Biaya Eksternal) / Total Perekrutan.
- A (Dapat dicapai): Hal ini dapat dicapai dengan meningkatkan persentase perekrutan dari sumber berbiaya rendah tetapi berkualitas tinggi, khususnya menargetkan peningkatan rujukan karyawan yang berhasil sebesar 25%, serta berinvestasi dalam konten branding pemberi kerja organik.
- R (Relevan): Sasaran ini relevan dengan inisiatif penghematan anggaran Q3/Q4 perusahaan dan membebaskan sumber daya untuk program pengembangan bakat lainnya.
- T (Terikat waktu): Pada akhir tahun fiskal ini.
- Sasaran SMART Akhir: “Turunkan rata-rata Biaya per Perekrutan untuk posisi non-eksekutif sebesar 15% (menjadi $3.400) pada akhir tahun fiskal, dengan meningkatkan total perekrutan dari program rujukan karyawan sebesar 25%.”
4. Enhance the Candidate Experience
- Tujuan Umum: Tingkatkan proses lamaran dan wawancara untuk membangun merek pemberi kerja yang lebih kuat dan menarik bakat yang lebih baik.
- S (Spesifik): Meningkatkan pengalaman kandidat untuk semua pelamar yang mencapai tahap wawancara formal.
- M (Terukur): Tingkatkan skor Kepuasan Kandidat (CSAT) rata-rata dari 3,5/5 menjadi 4,5/5, yang diukur melalui survei umpan balik pasca-wawancara otomatis.
- A (Dapat dicapai): Hal ini dapat dicapai dengan menerapkan kebijakan “no-ghosting” yang menjamin semua kandidat yang diwawancarai menerima tanggapan formal, dan dengan menyediakan satu titik kontak untuk komunikasi yang jelas dan konsisten.
- R (Relevan): Hal ini relevan untuk memperkuat citra pemberi kerja dan meningkatkan Tingkat Penerimaan Tawaran, karena kandidat yang mempunyai pengalaman positif lebih besar kemungkinannya untuk menerima.
- T (Terikat waktu): Pada akhir Q3.
- Sasaran SMART Akhir: “Tingkatkan skor Kepuasan Kandidat (CSAT) rata-rata untuk pelamar tahap wawancara dari 3,5 menjadi 4,5 pada akhir Q3, dengan menerapkan kebijakan 'tanpa ghosting' dan memastikan komunikasi yang konsisten dan jelas.‘
5. Increase Diversity And Inclusion (DEI)
- Tujuan Umum: Bangun tim yang lebih beragam dan pastikan proses perekrutan yang adil dan inklusif.
- S (Spesifik): Meningkatkan representasi kaum minoritas yang kurang terwakili (URM) dalam jalur bakat kepemimpinan (tingkat Direktur dan di atasnya).
- M (Terukur): Meningkatkan representasi dalam jalur ini dari 18% saat ini menjadi 25%, sebagaimana diukur berdasarkan laporan keberagaman internal tahunan.
- A (Dapat dicapai): Hal ini dapat dicapai dengan mewajibkan beragam panel wawancara untuk semua peran kepemimpinan dan secara proaktif memperluas kemitraan sumber daya dengan jaringan profesional, organisasi, dan universitas yang berfokus pada bakat URM.
- R (Relevan): Sasaran ini relevan dengan komitmen DEI publik perusahaan dan penting untuk mendorong inovasi dengan menghadirkan beragam perspektif ke dalam kepemimpinan.
- T (Terikat waktu): Pada akhir akhir tahun 2025.
- Sasaran SMART Akhir: “Tingkatkan representasi URM dalam jalur talenta tingkat Direktur ke atas dari 18% menjadi 25% pada akhir tahun 2025, dengan menerapkan panel wawancara yang beragam dan memperluas kemitraan sumber daya dengan jaringan profesional.”.
Templat Penetapan Sasaran Rekrutmen SMART Gratis Anda (Lembar Kerja)
Cara Menggunakan Template Ini
Lembar kerja ini merupakan alat bantu untuk bertindak. Salin tabel di bawah ini dan gunakan pertanyaan panduan, yang didasarkan pada metodologi penetapan tujuan yang telah ditetapkan, untuk menguraikan tujuan umum menjadi tujuan SMART yang dapat ditindaklanjuti. Isi setiap kotak untuk memperjelas pemikiran tim dan membuat pernyataan tujuan akhir yang selaras.
Tabel Lembar Kerja Sasaran SMART
| Komponen | Pertanyaan Panduan | Tujuan Anda (Dengan Contoh) |
| Tujuan Umum: | Tantangan tingkat tinggi atau kebutuhan bisnis apa yang sedang Anda tangani? | Tingkatkan efisiensi perekrutan dengan mengurangi penundaan dalam mengisi posisi yang terbuka. |
| Sspesifik | Apa sebenarnya yang ingin Anda capai? Siapa saja yang terlibat? | Mengurangi rata-rata waktu untuk mengisi untuk semua peran teknis. Tim Akuisisi Bakat (TA) Dan manajer perekrutan akan berkolaborasi untuk memperlancar proses pencarian sumber dan wawancara. |
| Mdapat diukur | Bagaimana Anda mengukur kesuksesan? Apa KPI dan target spesifiknya? | Kurangi waktu rata-rata untuk mengisi dari 45 hari hingga 30 hari, dilacak melalui Analisis ATS secara bulanan. |
| Adapat dicapai | Mungkinkah ini terjadi? Tindakan atau sumber daya baru apa yang dibutuhkan? | Ya. Hal ini dapat dicapai dengan menerapkan Alat sumber daya bertenaga AI, mengotomatiskan penyaringan kandidat, dan memperluas program rujukan karyawan untuk menarik kandidat yang berkualifikasi lebih cepat. |
| Rrelevan | Mengapa hal ini penting? Bagaimana hal ini selaras dengan tujuan perusahaan? | Sejalan dengan tujuan perusahaan untuk mempercepat pengembangan produk Dan meningkatkan efisiensi operasional dengan mengisi peran teknis dengan cepat, memastikan proyek tetap sesuai jadwal. |
| Tterikat waktu | Kapan tenggat waktunya? Apa saja tonggak pencapaiannya? | Implementasi lengkap dan mencapai target pengurangan dalam waktu 6 bulan (akhir Q2). Tinjau kemajuan setiap bulan dan sesuaikan saluran sumber jika diperlukan. |
| Sasaran SMART Akhir: | [Gabungkan semua elemen menjadi satu pernyataan yang jelas] | “Kurangi waktu rata-rata pengisian untuk semua peran teknis dari 45 hari menjadi 30 hari pada akhir Q2, dengan menerapkan perangkat pencarian AI dan memperluas program rujukan karyawan untuk mempercepat penyaringan kandidat dan mencegah hilangnya talenta terbaik.” |
Key Recruitment Metrics (KPIs) to Track
“M” (Terukur) dalam SMART membutuhkan perangkat yang kuat metrik akuisisi bakat. KPI ini adalah bahasa tim rekrutmen berbasis data. KPI secara umum dapat dikategorikan menjadi dua jenis: metrik proses yang melaporkan apa yang terjadi dan metrik strategis yang membantu memprediksi apa yang akan terjadi.
Metrik Proses (Indikator Tertinggal)
- Waktu Pengisian: Ini mengukur total jumlah hari sejak permintaan pekerjaan dibuka hingga tawaran diterima. Ini adalah metrik utama untuk efisiensi proses secara keseluruhan.
- Waktu Perekrutan: Metrik yang lebih berfokus pada kandidat ini mengukur jumlah hari sejak kandidat melamar atau pertama kali dihubungi hingga mereka menerima tawaran. Metrik ini mengukur kecepatan perjalanan kandidat.
- Biaya per Perekrutan (CPH): Ini adalah total investasi finansial untuk satu kali perekrutan. Rumus standarnya adalah: (Total Biaya Internal + Total Biaya Eksternal) / (Total # Perekrutan).
- Attrition Tahun Pertama (Omzet): Ini adalah persentase karyawan baru yang keluar secara sukarela atau tidak sukarela dalam 12 bulan pertama mereka. Ini merupakan indikator tertinggal yang penting dari Kualitas Karyawan.
Metrik Strategis (Indikator Utama)
- Kepuasan Kandidat (CSAT): Biasanya diukur melalui survei otomatis yang dikirim setelah wawancara atau di akhir proses, metrik ini melacak pengalaman kandidat. Ini merupakan indikator utama yang kuat untuk menilai kesehatan merek perusahaan.
- Tingkat Penerimaan Penawaran (OAR): Ini adalah persentase penawaran lanjutan yang diterima. OAR yang rendah merupakan tanda bahaya kritis yang menunjukkan bahwa kompensasi, tunjangan, atau proses itu sendiri tidak kompetitif.
- Efektivitas Saluran Sumber: Metrik ini melacak persentase kandidat yang memenuhi syarat atau, yang lebih penting, perekrutan yang berasal dari setiap saluran (misalnya, LinkedIn, rujukan, papan pekerjaan). Analisis ini menunjukkan di mana sebaiknya menginvestasikan waktu dan uang.
Kualitas Penyewaan (QoH) – The “North Star” Metric
Banyak pakar akuisisi talenta menganggap Kualitas Perekrutan (QoH) sebagai "standar emas" dan metrik terpenting. Hal ini karena QoH merupakan ukuran utama apakah proses rekrutmen memberikan nilai jangka panjang bagi organisasi.
Namun, QoH bukanlah KPI tunggal dan universal. Ini adalah dasbor komposit khusus yang harus didefinisikan oleh setiap organisasi untuk dirinya sendiri. Langkah pertama untuk melacak QoH adalah mendefinisikan maknanya bagi perusahaan. Metrik QoH yang paling efektif adalah kombinasi dari:
- Kinerja Karyawan Baru: Diukur berdasarkan peringkat tinjauan kinerja 6 atau 12 bulan.
- Retensi Karyawan Baru: Diukur berdasarkan tingkat pergantian karyawan selama 1 tahun.
- Kepuasan Manajer Perekrutan: Diukur melalui survei pasca-perekrutan selama 90 hari.
Pertanyaan yang Sering Diajukan (FAQ) tentang Tujuan Rekrutmen
1. What are some examples of recruitment goals for 2026?
Top recruitment goals for 2026 are focused on efficiency, quality and intelligence. They include elevating the quality of hire, speeding up the hiring process (reducing time-to-hire), increasing diversity and inclusion in leadership, enhancing employer branding and strategically leveraging AI in the recruitment workflow for sourcing and screening.
2. How are recruitment goals different from recruitment KPIs?
Tujuan rekrutmen adalah tujuan spesifik tujuan you want to achieve (for example, “Reduce time-to-hire“). Recruitment KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are the metrik Anda gunakan untuk mengukur kemajuan Anda terhadap that goal (for example, “Time-to-hire in days“). A well-written goal will contain its own KPI.
3. How many recruitment goals should I set?
Sebaiknya fokus pada 3-5 tujuan berprioritas tinggi per kuartal atau tahun. Tujuan-tujuan ini harus selaras langsung dengan kebutuhan bisnis terpenting organisasi. Dampak dan fokus jauh lebih penting daripada daftar tujuan yang panjang.
4. What is the most important recruitment goal?
Meskipun hal ini bergantung pada tantangan spesifik yang dihadapi suatu organisasi (misalnya, perusahaan dengan pemotongan anggaran mungkin memprioritaskan CPH), banyak ahli mempertimbangkan Kualitas Penyewaan (QoH) the “gold standard” or most important metric. This is because it is the ultimate measure of whether the recruitment process is successfully delivering high-performing employees who drive long-term business value.
Mulailah Membangun Proses Perekrutan yang Lebih Cerdas dan Cepat Hari Ini
The shift from reactive “fire-fighting” to strategic, goal-oriented talent acquisition is the most impactful change a recruiting team can make. Moving from vague ambitions like “hire faster” to a data-driven, SMART goal like “Reduce Time-to-Fill for technical roles from 45 to 30 days by Q3” provides clarity, enforces alignment and delivers a measurable return on investment. This framework is the first step to ending the vicious hiring cycle, proving the TA team’s strategic value and building a high-performing, resilient workforce.
Siap melacak tujuan baru Anda secara otomatis? Platform akuisisi bakat yang efektif menyediakan dasbor instan untuk waktu pengisian, kualitas rekrutmen, dan efektivitas saluran sumber daya. Pesan demo bersama tim easy.jobs untuk melihat cara mengubah data menjadi keunggulan rekrutmen yang strategis. Jika Anda merasa artikel ini bermanfaat, berlangganan blog kami dan bergabung dengan kami Komunitas Facebook untuk menemukan informasi mendalam dan berita terkini di industri dan di antara sesama perekrut.






