Hiring bias silently shapes who gets hired and who gets overlooked often without anyone realizing it. These hidden patterns do not just hurt candidates. They weaken hiring outcomes, diversity and business growth.
Are you curious how bias creeps into recruitment decisions and what you can actually do to stop it? This guide breaks down the causes, examples and proven ways to eliminate hiring bias for good.
TL;DR: Key Takeaways from This Guide
Below is a quick snapshot of the most important points covered in this guide:
- Hiring bias happens when personal opinions, often without realizing it affect hiring decisions instead of skills and experience.
- It can negatively impact pengalaman kandidat, workplace diversity, legal compliance and overall hiring quality.
- Hiring bias can be identified through regular reviews of hiring data and reduced by using structured processes, fair evaluations, technology, and proper training.
The sections below explore these ideas in detail and explain how to build a fair, consistent, and unbiased hiring process.
What Is Hiring Bias?
Hiring bias means making hiring decisions based on personal opinions or assumptions instead of a candidate’s skills, experience, and ability to do the job. This bias can happen at any stage of recruitment and often without the recruiter even realizing it.
Hiring Bias Definition in Recruitment
In simple terms, hiring bias happens when a recruiter favors or rejects a candidate for reasons that are not job-related. These reasons might include a person’s name, age, gender, background, or where they come from.
Hiring bias is not the same as diskriminasi tempat kerja. Discrimination is usually intentional and illegal, while hiring bias is often unintentional and driven by habits, past experiences, or personal comfort. Many recruiters do not mean to be unfair. Bias happens naturally unless steps are taken to prevent it.
Conscious vs Unconscious Bias in Recruitment
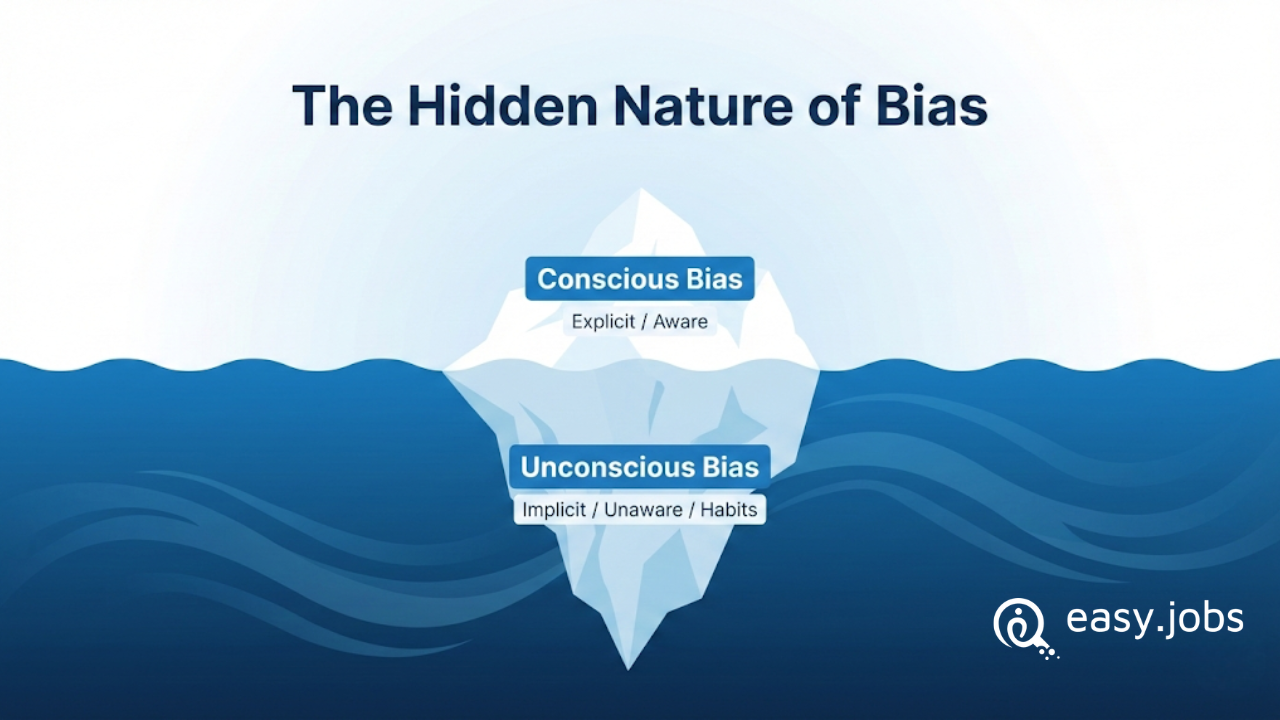
There are two main types of hiring bias:
- Conscious (explicit) bias happens when someone is aware of their preference or judgment.
- Unconscious (implicit) bias happens automatically, without awareness.
Unconscious bias is more common in hiring. Recruiters often use mental shortcuts to make quick decisions, especially when reviewing many candidates. These shortcuts can lead to unfair choices, which is why unconscious bias is harder to notice and control.
Stages of the Hiring Process Where Bias Occurs
Hiring bias can appear at multiple stages of recruitment, including:
- Resume screening: Judging candidates based on names, schools, gaps in employment, or location
- Interviews: Being influenced by first impressions, accents, or personal similarity
- Assessments and final decisions: Favoring candidates who “feel right” rather than those who score best on skills
Understanding where bias shows up is the first step toward reducing it and building a fair hiring process.
Why Hiring Bias Happens?
Hiring bias does not usually happen because recruiters want to be unfair. It happens because of how people think and how hiring processes are designed. Human psychology and weak recruitment structures together create space for biased decisions.
Human Psychology and Cognitive Bias
The human brain looks for patterns to make decisions quickly. These mental shortcuts help save time, but they can also lead to mistakes. In recruitment, this often shows up as cognitive bias.
Recruiters may rely on a “gut feeling” when choosing candidates, especially under pressure. While instincts can feel helpful, they are often influenced by past experiences, familiarity, or personal comfort, not actual job-related evidence. This is why gut-based hiring can lead to biased decisions instead of fair, skill-based ones.
Structural Gaps in Recruitment Processes
Hiring bias becomes more likely when recruitment processes lack structure. For example:
- Unstructured interviews allow different candidates to be judged by different standards
- Vague job descriptions leave room for personal interpretation of what “good” looks like
- Subjective evaluation criteria make it easier to favor opinions over facts
When clear rules and standards are missing, personal bias fills the gap. Strong, structured hiring processes help reduce this risk.
Types of Hiring Bias dalam Perekrutan
Hiring bias can take many forms, and some are easier to notice than others. Understanding the different types of hiring bias helps recruiters and hiring managers recognize unfair patterns and make better, more balanced decisions.
Most Common Hiring Biases

These are some of the most common hiring biases seen in recruitment:
- Affinity bias: Favoring candidates who are similar to you in background, interests, or personality
- Confirmation bias: Looking for information that supports your first impression and ignoring facts that don’t
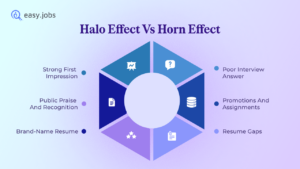
- Halo and horns effect: Letting one positive trait (halo) or one negative trait (horns) influence your entire view of a candidate
- Gender bias: Making assumptions about a candidate’s ability or role fit based on gender
- Racial bias: Judging candidates based on race or ethnicity instead of skills
- Age bias (ageism): Favoring younger or older candidates based on stereotypes rather than experience
Hidden and Overlooked Hiring Biases
Some biases are subtle and often go unnoticed, but they still affect hiring decisions:
- Name bias: Making assumptions based on a candidate’s name
- Accent bias: Judging communication skills or intelligence based on accent
- Location bias: Favoring candidates from certain cities, regions, or countries
- Educational bias: Valuing certain schools or degrees more than actual skills and performance
Real-World Hiring Bias Examples
Hiring bias often shows up in everyday recruitment situations, such as:
- Rejecting resumes because the candidate does not come from a “preferred” school
- Rating a candidate higher because they “feel like a good fit” without clear reasons
- Overlooking qualified candidates due to age, name, or background
Recognizing these examples is an important step toward reducing bias and building a fair hiring process.
Impact of Hiring Bias on Businesses and Candidates
Hiring bias does not just affect who gets hired. It also has long-term effects on candidates, companies and overall workplace culture. When bias goes unchecked, everyone loses.
Impact on Candidate Experience
Candidates can often sense when a hiring process is unfair. When decisions seem biased:
- Qualified candidates may feel overlooked or treated unfairly
- Many candidates drop out of the process early
- Trust in the employer decreases, harming the company’s reputation
A biased hiring experience can discourage talented people from applying again or recommending the company to others.
Business and Organizational Impact
Hiring bias can lead to poor business outcomes, including:
- Poor quality of hire: The best candidate may be missed due to personal bias
- Reduced diversity and innovation: Teams made up of similar people often lack fresh ideas and perspectives
- High employee turnover: Poor hiring decisions increase the chances of early exits and rehiring costs
Over time, biased hiring weakens team performance and business growth.
Legal and Compliance Risks
Hiring bias can also create legal risks. Many countries have equal employment opportunity rules and employment discrimination laws that require fair hiring practices.
How to Identify Hiring Bias in Your Recruitment Process?
Hiring bias is not always obvious, but there are clear signs that can help you spot it. By looking closely at your hiring patterns and data, you can identify where bias may be affecting decisions.
Signs Your Hiring Process Is Biased
Some common warning signs include:
- Homogeneous teams: Most employees have similar backgrounds, ages, or profiles, even though the talent pool is diverse
- Inconsistent interview feedback: Different interviewers give very different opinions about the same candidate without clear reasons
These patterns often suggest that personal judgment is influencing decisions more than clear criteria.
Auditing Recruitment Data for Bias
Hiring data can reveal bias that isn’t visible on the surface. Reviewing key metrics helps you understand where candidates drop off or are treated differently.
This includes looking at:
- Resume-to-interview ratios: Who gets shortlisted and who does not
- Recruitment funnel analysis: Where candidates exit the process
- Offer acceptance by demographic: Whether certain groups receive or accept offers less often
Regularly reviewing these numbers helps detect bias early and improve fairness in hiring.
How to Reduce and Eliminate Hiring Bias?
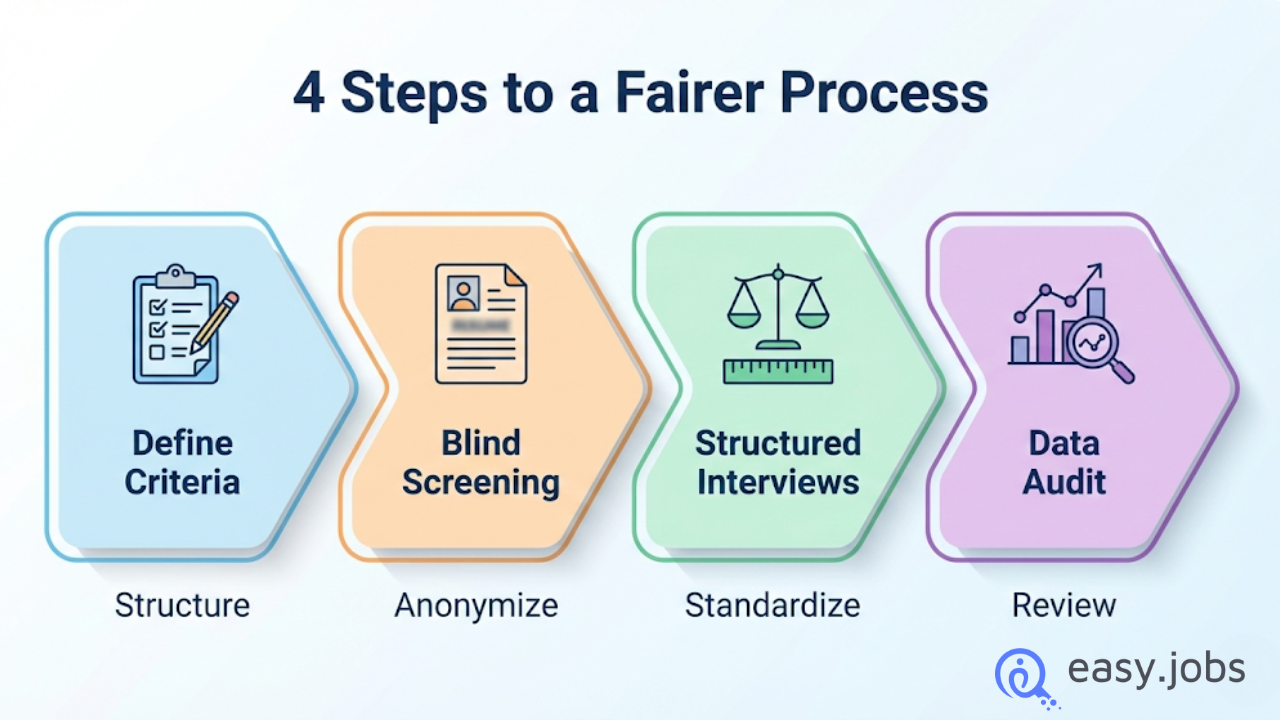
Reducing hiring bias requires clear processes, fair evaluation methods, and the right use of technology. When hiring decisions are based on skills and evidence, not personal opinions. Bias becomes much harder to influence outcomes.
Structured Hiring and Standardization
A structured hiring process ensures every candidate is evaluated in the same way.
- Structured interviews use the same set of questions for all candidates
- A standardized hiring process applies clear criteria at each stage
This consistency helps remove guesswork and personal preference from decisions.
Bias-Free Resume Screening
Bias often starts during resume review. Two effective ways to reduce it are:
- Blind resume screening: Removing names, photos, age, or location from resumes
- Skills-based hiring: Focusing on abilities and experience rather than background or credentials
These methods help recruiters judge candidates based on what truly matters.
Reducing Interview Bias
Interviews can be more fair and objective with the right structure:
- Pertanyaan wawancara perilaku focus on real examples of past work
- Interview scorecards help interviewers rate candidates using the same standards
- Panel interviews reduce the influence of a single person’s opinion
Together, these practices create more balanced hiring decisions.
Role of Technology in Bias Reduction
Technology can support fair hiring when used carefully.
- ATS platforms help standardize screening and track decisions
- AI tools can reduce manual bias but may also reflect biased data
Because of this, human oversight is essential. Technology should support decision-making, not replace responsible human judgment.
Building Fair and Inclusive Hiring Practices Long-Term
Reducing hiring bias is not a one-time effort. To create lasting change, companies need long-term, fair, and inclusive hiring practices that are followed consistently across teams.
Training Recruiters and Hiring Managers
Training helps hiring teams understand how bias works and how to control it.
- Unconscious bias training helps recruiters recognize hidden preferences that affect decisions
- Calibration sessions align hiring managers on what “good” looks like and how candidates should be evaluated
Regular training keeps hiring decisions focused on skills and job requirements.
Policy, Documentation, and Accountability
Clear rules and documentation help ensure fairness in hiring.
- Hiring playbooks outline step-by-step hiring standards and best practices
- Decision transparency means documenting why candidates are shortlisted or rejected
Hiring Bias vs. Fair Hiring
When decisions are clear and accountable, hiring becomes more consistent, fair, and inclusive over time.
Hiring bias and fair hiring differ mainly in how decisions are made and what recruiters focus on during the hiring process. The table below highlights the key differences between the two approaches.
| Aspek | Biased Hiring | Fair Hiring |
| Decision style | Based on gut feelings and personal opinions | Based on clear rules and structured processes |
| Evaluation method | Subjective and inconsistent | Objective and consistent for all candidates |
| Kecepatan perekrutan | Faster in the short term | Slightly slower but more accurate |
| Candidate assessment | Influenced by first impressions or familiarity | Focused on skills, experience, and job fit |
| Diversity outcome | Low diversity and similar profiles | More diverse and inclusive teams |
| Long-term results | Poor hires and high turnover | Better hires and long-term success |
Moving toward fair hiring may take more effort at the start, but it leads to stronger teams, better hiring decisions, and long-term business growth.
FAQs About Hiring Bias
Below are some common questions people ask about hiring bias, along with simple and clear answers.
What is hiring bias?
Hiring bias happens when hiring decisions are influenced by personal opinions or assumptions instead of a candidate’s skills and ability to do the job. It often happens without realizing it.
Is hiring bias the same as discrimination?
No. Discrimination is usually intentional and illegal. Hiring bias is often unintentional, but it can still lead to unfair outcomes if not addressed.
What is the most common hiring bias?
One of the most common hiring biases is affinity bias, where recruiters prefer candidates who are similar to themselves in background, personality, or experience.
How do recruiters avoid unconscious bias?
Recruiters can reduce unconscious bias by using structured interviews, clear evaluation criteria, blind resume screening, and regular bias-awareness training.
Can AI remove hiring bias completely?
No. AI can help reduce some types of bias, but it can also repeat bias from past data. Human review and oversight are still necessary.
Why is fair hiring important for businesses?
Fair hiring helps companies find the best talent, build diverse teams, improve employee retention, and reduce legal and reputational risks.
Take Control of Hiring Bias Through Smarter Hiring Practices
Hiring bias in recruitment is not about bad intentions. It is a systemic issue that appears when decisions are unstructured and subjective. Bias affects who gets hired, team diversity, and overall hiring quality.
The most effective way to reduce bias is to build an unbiased hiring process using clear structure, consistent evaluation, and data-driven decisions. When hiring is guided by defined criteria instead of personal opinions, fairness improves and better talent outcomes follow. If you found this guide helpful, berlangganan blog kami for more practical insights on fair and effective hiring. You can also join our komunitas Facebook to connect with others, share your thoughts, and stay updated on the latest recruitment best practices.